If you are a Doctor who plans to work in Ireland, it’s important to understand how to verify your documents so you can register with the Irish Medical Council (IMC). EPIC is a service that verifies whether your medical qualifications meet international standards. The Irish Medical Council (IMC) uses this verification to ensure that your education and training are equivalent in quality to those in Ireland.
Without EPIC verification, your application could be delayed or even rejected. That’s why it’s important to understand and complete this process correctly. This blog provides a step-by-step guide to help you through the process.
How To Verify Your Credentials
1. Confirm Your Medical School Listing
Start by ensuring your medical school is listed in the World Directory of Medical Schools. Only graduates from listed institutions are eligible for registration.
2. Set Up Your Account
Go to the EPIC website and create your account. After EPIC processes your application, they will email your login details. Use these credentials to access your personal EPIC dashboard, where you can upload documents and manage all requests. You’ll need to pay a registration fee when you submit your account request.
3. Verify Your Identity
Before uploading any credentials, you will need to submit an EPIC Identification Form (EIF) and confirm your identity. This one-time identity verification unlocks your ability to upload documents for verification.
The required documents can change based on where you completed your training. They also depend on whether you are applying for an exemption for your Medical Council Training. You can find more details on the Medical Council website.
4. Upload Required Credentials for Medical Council Ireland
Upload all necessary documents, such as your Final Medical Degree or Diploma, Internship Certificate, and any other educational documents. Be sure to select the Irish Medical Council as the recipient when uploading each document. This ensures that the system automatically sends your EPIC Report to the IMC once the verification process is complete.
If ECFMG has already verified your documents, you can add them to your EPIC portfolio for free. Just make sure to include your ECFMG/USMLE ID when setting up your account.
5. Apply for IMC Registration
After you verify and send all required documents, finish submitting your application to register with the Irish Medical Council. Submit the official form on the Medical Council’s website. Include your EPIC ID in the application to link your verified documents to your submission.
6. Check That All Reports Are Sent
You can manage and track reports through the “My Reports” tab in your EPIC account. If you didn’t select the Irish Medical Council as the recipient when uploading a document, you need to go to your EPIC account and send the report to them manually to make sure they receive it.
7.Finalise Your Medical Registration
Once you have confirmed that all your documents and reports are submitted correctly to the IMC, you can proceed with the next steps in the registration process. Depending on the type of registration you apply for, you may need to complete additional requirements, such as passing a pre-registration examination.
Once you meet all the requirements and the IMC approves your application, you will be officially registered and ready to begin practicing medicine in Ireland.
Summary
Using EPIC to verify your medical credentials is a key part of the IMC registration process for international Doctors. With your EPIC login, you can control your document submissions and manage your application form. This ensures a smooth path to practicing medicine in Ireland.
This blog provides a comprehensive guide for Doctors looking to practice in Ireland, covering everything from studying medicine at university to registering with the Irish Medical Council (IMC). It highlights the various medical roles available, including internships, Non-Consultant positions, and Consultancy, and offers key information for Doctors considering relocation to Ireland.
How Many Years Does it Take to become a Doctor in Ireland
Typically, it takes 5–6 years to study medicine in Ireland, followed by at least one year of internship and additional years for specialisation.
For international Doctors, the process remains similar, though additional steps may be required for recognition of qualifications and ensuring English proficiency.
Career Pathways for Doctors in Ireland
Interns in Ireland
An Intern is a Doctor who is in their first year after medical school. The intern year is essential in gaining hands-on experience in a clinical setting. During this 12-month period, Interns rotate through multiple specialties. Upon completing the internship, the Medical Council of Ireland (MCI) grants a Certificate of Experience, which allows graduates to apply for general registration or trainee specialist registration.
Non – Consultant Hospital Doctors (NCHD’s)
A Non-Consultant Hospital Doctor (NCHD) is a Doctor who works under the guidance and observation of a Consultant.
Senior House Officers (SHO’s)
A Senior House Officer (SHO) is a type of Non Consultant Hospital Doctor (NCHD) who is supervised by Registrars and Consultants. SHOs typically work under Consultants or Registrars in hospitals across Ireland. SHOs can either be in training posts or non-training positions. Those in SHO jobs in Ireland who are not enrolled in a postgraduate training scheme are referred to as non-training SHOs.
Registrars
A Registrar is a Doctor who has completed a minimum of 24 months post-internship. They work under the supervision of Consultants and are gaining experience in their specialty. Registrar Doctors working in Ireland can be in training or non-training posts, depending on their long term career goals.
Specialist Registrar
The next step up is a Specialist Registrar (SpR), who is in the final stage of specialist training. A specialist is in a position where they have a high level of responsibility but are still in a training programme. An SpR is part of a postgraduate training program in one of over 40 specialties across Ireland. Upon completion, the Doctor is awarded a Certificate of Satisfactory Completion of Specialist Training (CSCST), qualifying them for Consultant posts.
Consultants
A Consultant is a fully qualified Senior Doctor who has completed their training and have become an expert in their field.
Locum Doctors
A Locum Doctor is a temporary Doctor who fills in for absent colleagues. Locum positions are common in Ireland and are available across various specialties. Locum Doctor jobs in Ireland provide flexibility and an opportunity to work in different healthcare settings. To be eligible you need to be an Irish, EU or UK citizen or resident and be eligible to work in Ireland without a work permit.
Irish Medical Council Registration
To practice medicine in Ireland, all Doctors must have IMC registration.There are different types of registration and requirements. For a full guide on registration see our complete guide to IMC registration.
General Registration
If you have completed a recognised medical degree, you can register for General Registration. This allows you to work as a Doctor in Ireland without supervision. If you have trained outside of the EU/EEA please see our blog on Relocating to Ireland as a Doctor .
Specialist Registration
Specialist Registration allows Doctors to practice independently as a Specialist/Consultant in their field of specialisation.
English Language Proficiency
All NCHDs and medical professionals must demonstrate proficiency in English to meet the communication standards required for patient care in Ireland. Accepted proof includes a degree from an English-speaking country, such as the UK, USA, Canada, Australia. Alternatively, an International English Language Testing System (IELTS) or Occupational English Test (OET). This can also be evidenced by studying medicine in English or working in an English speaking country for 2 years out of the last 5.
Police Clearance & Garda Vetting
Before starting employment, all Doctors in Ireland are required to undergo police clearance, also known as Garda Vetting. This ensures that healthcare professionals do not pose a risk to patients or the public. Additionally, if a Doctor has worked/lived outside Ireland within the last 10 years, they must provide an overseas police clearance from all countries they’ve worked in.
Working in the Irish Healthcare System
Public Hospitals
Public hospitals in Ireland are owned and funded by the Health Service Executive (HSE), which provides health and social services throughout the country. The hospitals are categorised into statutory and voluntary public hospitals. Statutory hospitals are fully funded by the government, while voluntary hospitals receive state funding but may be managed by private bodies.
Private Hospitals
Private hospitals in Ireland operate independently of the HSE and do not receive state funding. These hospitals offer private healthcare services for patients who prefer to pay for care.
How to set up in Ireland: Banking, PPSN, and Accommodation
Setting Up a Bank Account in Ireland
To open a bank account in Ireland, you will need proof of address (e.g., utility bills, rental agreements), photo identification (passport or driver’s license). A Personal Public Service Number (PPSN) is essential for setting up a bank account in Ireland. It’s used for taxation, social services, and employment purposes. Most banks will require this to complete the account-opening process.
How to Get a PPS Number
The Personal Public Service Number (PPSN) is vital for accessing public services and you will need it for everything from getting paid to filing taxes or applying for government services like healthcare. You can apply for a PPSN number online.
Having a PPS number allows you to:
- Be taxed correctly by your employer.
- Access healthcare services and apply for social welfare benefits.
- Register with various public and private services in Ireland.
Finding Accommodation as an International Doctor in Ireland
Finding accommodation in Ireland can be challenging, especially in major cities like Dublin, Cork, and Galway, where demand often exceeds supply. Rent prices have been rising steadily in recent years, making it important to budget carefully.
Many cities, such as Dublin, Cork, and Galway, offer a range of rental options, from shared apartments to private homes. It’s advisable to start your search early, especially in larger cities where demand is high. Websites like Daft.ie and Rent.ie are popular platforms to find listings.
You will typically need proof of income, a reference, and a deposit to secure a place. Consider proximity to your hospital or medical facility, as well as public transportation options. Many international Doctors opt for short-term rentals initially while they settle in and search for longer-term accommodation.
Conclusion
Becoming a Doctor in Ireland offers rewarding opportunities in a well-structured healthcare system. From a career as a General Practitioner to a Specialist Registrar, there is a wide range of positions available for Doctors looking to practice in Ireland.
If you’re considering a move to Ireland, explore the different roles available and ensure you’re fully prepared to take the necessary steps for a successful medical career.
Are you a Doctor interested in working as a Locum GP in Ireland? Locum work provides great flexibility and promotes a healthy work life balance. This blog outlines everything you need to know about working as a Locum GP in Ireland.
What is a Locum GP?
A Locum GP is a medical professional who temporarily replaces another Doctor when they are unavailable due to illness, vacation, or leave. Locum Doctors can work in a number of healthcare settings, including general practices and filling in for General Practitioners (GPs). This short term role offers flexibility, allowing Doctors to work for short periods without committing to a long-term position.
How to Become a Locum Doctor in Ireland
Becoming a Locum Doctor in Ireland can be a rewarding career choice. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to get started:
Understand the Requirements for the Irish Medical Council Register
Before you can work as a Doctor in Ireland, you need to be registered with the Irish Medical Council (IMC). Being listed in the IMC register is essential for Doctors in Ireland, as it maintains the official register of medical professionals in the country. To become registered, you will need to meet certain criteria depending on your qualifications and country of origin.
Gather Your Documentation
To apply for registration with the IMC, you will need the following:
- Proof of your medical degree
- A valid passport
- Proof of English language proficiency (IELTS or equivalent)
- Details of any previous work experience or internships
- Any additional documentation as specified by the Medical Council of Ireland.
Complete the IMC Registration Process
Once you have your documentation ready, you can apply for registration. There are different types of registration depending on your qualifications. For example, if you are an international medical graduate, you may need to undergo a period of supervised practice before you can obtain general registration.
You can apply for Medical Council registration online through the Medical Council Ireland Registration page, where you can track your application status. Should you wish to practice as a Locum Doctor in any specific specialty, the IMC must evaluate your qualification before they can grant specialist registration. IMC registration is crucial for Locum Doctors as it ensures they are legally recognised to practice medicine in Ireland.
How Much Do Locum Doctors Get Paid?
The pay for Locum Doctors varies depending on experience, location, and the healthcare setting. However, a Locum Doctor salary in Ireland is generally higher than a regular full-time position. Locum Doctors are typically self employed and have the flexibility to take Locum positions as they wish.
Rates can vary based on the need for healthcare in certain areas and based on the level of experience required. It is important to note that Junior Doctors cannot work as Locum GPs until they have completed their GP training and become fully qualified GPs. However, Junior Doctors can do Locum work in other specialties in hospitals before completing their GP training.
The Benefits of Locum GP Work
Variety:
As a Locum Doctor you will have the opportunity to work across a range of healthcare settings and engage with a diverse range of patients. Locum GPs can gain exposure to different healthcare systems and insight into how different types of patient care is delivered.
Flexibility:
One of the largest benefits associated with Locum work is the flexibility to choose your own schedule.This improves work life balance and allows you to choose what works for you fostering a healthy lifestyle.
Networking:
Working as a Locum Doctor helps you build a strong network of contacts, creating valuable connections across both the HSE and private practices. This can lead to a high demand for your services.
The Importance of Insurance
As a Locum GP in Ireland, it is essential to obtain medical malpractice insurance before practicing independently. This insurance protects you from claims of negligence or malpractice that could arise during your work. It covers the costs of legal defense and any potential compensation if a claim is made against you.
Conclusion
Becoming a Locum Doctor can be an excellent choice for those looking for flexibility and variety in their work. By following the necessary steps for registration, obtaining the proper credentials, and finding the right jobs, you can quickly establish a fulfilling career in Ireland.
The demand for healthcare professionals is always growing, and the flexibility of locum work can provide a great balance of career satisfaction and lifestyle. Whether you’re considering a full-time commitment or seeking a temporary position, working as a Locum Doctor offers dynamic opportunities and a rewarding pathway. For more information about opportunities as a Locum Doctor in Ireland, don’t hesitate to contact us at Medforce.
To practice medicine in Ireland, doctors must register with the Irish Medical Council (IMC). This guide covers everything you need to know about the IMC registration process, including fees, requirements, and contact information. This information applies to both international doctors and Irish graduates who might be registering for the first time.
The Irish Medical Council (IMC) is the regulator of the medical profession in Ireland. It holds a record of licensed doctors and can take away or limit their license if there are concerns about their ability to practice.
The IMC maintains two registers, the General Register of Medical Practitioners and the Register of Medical Specialists.
What are the Different Types of Medical Registration?
General Registration
Irish Medical Council General Registration allows doctors to work as an NCHD (non-consultant hospital doctor).
You can apply for registration with the Irish Medical Council (IMC) in different ways, based on where you trained and worked.
Applicants fall into 4 main categories:
- Graduates from Irish Medical Schools
- EU Citizens who graduated in an EU Medical School and/or have qualifications recognised under EU Directives
- Non-EU citizens who graduated from an EU medical school or have qualifications accepted in the EU.
- Doctors who do not fall into any of the categories listed above.
Applicants in Category 4 must pass the Pre-Registration Examination System (PRES) some might however be exempt and should check the registration rules and exemptions.
Specialist Registration
Specialist Registration allows a doctor to practice independently without supervision and represent themselves as specialists.
Application Routes
- Doctors who have completed higher specialist training in Ireland.
- Doctors who have trained and or recognised as a specialist in a European Union State.
- Any other Doctor may have their existing training and experience evaluated to gain registration.
IMC Registration Requirements
To be eligible for IMC Registration, you must meet specific requirements, including educational qualifications, language proficiency, and professional experience. Here are the main criteria:
Educational Requirements
To practice medicine in the Republic of Ireland, you must have completed a medical degree from a recognised institution. International doctors should check that the Irish Medical Council (IMC) recognises their medical degree.
This process includes reviewing their training and experience and using the document checklist provided on the IMC website.
IELTS Requirement for the Medical Council Register Ireland
Non-native English speakers must complete an English language test. One of the tests available is the IELTS exam. The IMC usually requires a minimum score of 7.0 in all parts of the IELTS exam.
This includes speaking, listening, reading, and writing. This exam ensures that doctors can communicate effectively with patients and colleagues in a healthcare setting. After successfully completing the test, they will become registered with the IELTS.
OET (Occupational English Test)
Non-native English speakers who want to work in the EU can take the OET (Occupational English Test). This test is for healthcare professionals. You need a B grade or higher to pass and register with OET.
Medical Council Ireland Registration Fees for Doctors
The registration fees differ depending on the type of registration you are applying for. Check the latest fee schedule on the official IMC register website before submitting your application form.
How to Apply for IMC Registration
If you are applying for IMC registration from outside the EU, EEA, or Switzerland, you must apply through EPIC (Electronic Portfolio of International Credentials).
To apply for IMC Registration within the EU the steps are as follows:
- Create an IMC Account
- Submit Your Documents provide your qualifications, proof of completed specialist training, certificate of experience, IELTS test results, and any other supporting documents.
- Pay the Registration Fees you will need to pay the registration fee through the IMC portal.
- Wait for IMC Approval & Medical Council Number Ireland once you apply, the IMC will check your documents and qualifications. If your application is approved, you will be added to the Irish Medical Council Register. Upon registration you will receive your Medical Council Registration number Ireland.
- Upon your registration, you can begin practicing medicine in Ireland under the applicable regulations and supervision.
Contacting the Irish Medical Council
If you have questions or need help with registration, you can contact the Medical Council of Ireland.
- Medical Council Ireland Contact Number: You can call their main office at +353 1 498 3100.
- Medical Council Ireland Contact Email: You can contact them using the form on their website. You can also email them directly at info@medicalcouncil.ie.
- Medical Council Ireland Login: Sign in to your IMC account. You can check your registration status or get help online.
Summary
For those aiming to practice medicine in Ireland, registering with the Medical Council is an essential requirement. The IMC Registration process makes sure that all doctors, both Irish-trained and international, meet the highest standards. This is important for providing safe and effective healthcare.
To register, review the Medical Council Ireland Register requirements carefully, ensure you meet the necessary criteria, and submit your application.
For more information, visit the Irish Medical Council website.
Medforce have been awarded Tier 2 status by the HSE for the provision of Locum Doctors nationwide.*
This means Medforce can now supply you with a wide array of locum work opportunities, allowing you to experience the flexibility and diversity that comes with temporary positions in various healthcare settings. Our locum roles offer the chance to travel and work in different locations across Ireland, and the opportunity to gain a broad spectrum of clinical experience.
Whether you’re looking to balance your personal life with professional commitments, seeking new challenges, or exploring different medical fields, Medforce’s locum opportunities provide the perfect platform to advance your career on your terms.
*Medforce is one of multiple Tier 2 suppliers, all agencies on the supplier panel pay the same hourly rates.
Benefits of Locum Work
- Flexible work hours to balance personal and professional life
- Weekly payments for Locum Doctors
- Opportunities for travel and working in different locations
- Short-term commitments offering career flexibility
- Networking with a broad range of healthcare professionals
- €150 referral bonus
Requirements
- Currently registered with the Irish Medical Council (IMC)
- Relevant medical qualification(s)
- Excellent communication and interpersonal skills – (IELTS/OET if required)
- Must have eligibility to do locum work in Ireland (EU/UK Passport or Valid IRP Stamp 4 / Stamp 1G)
In order to help place you in your dream job we will need you to put a little time into fine tuning your CV. To help you with this task we have included the highest priority elements to include below:
1 – Name
2 – Educational History
A chronological record (most recent first) of all formal educational programs, using the official name of the course, educational institution, date of award and the level of the award
3 – Professional Body Memberships and Registrations
Membership /Registration Name and date of conferral
4 – Working History
(Chronological order with the most recent first)
- Job title
- Name of Hospital and location
- Dates of employment
- Brief description of the hospital
- Duties and Responsibilities
5 – List of Clinical Skills
6 – Training History
A record of successfully completed training programs – official name of course and date certification received
7 – Research and Audits
Title and dates
8 – Publications
Article name, publication and date published
9 – Referee Details
- Referees name and job title
- Email Address
- Contact telephone number
General Registration Process
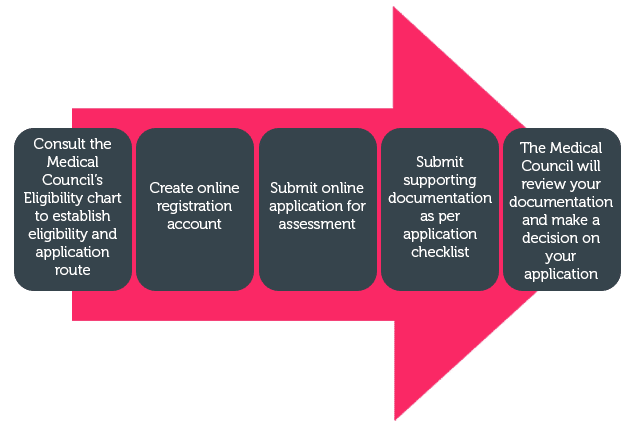
Doctors Trained Outside of the EU/EEA
If you have trained outside of the EU or EEA, you will need to have your medical education credentials verified through the Electronic Portfolio of International Credentials (EPIC) before you can apply for registration with the Medical Council. EPIC is hosted by the Educational Commission for Foreign Medical Graduates (ECFMG). You can learn more about how to use EPIC on the EPIC website.
There are 3 sub-routes in which you can apply for General registration as a Non-EU applicant:
- Higher Qualification
- Certificate of Experience
- Pre-Registration Examination System (PRES)
Eligibility Requirements:
Doctors who have a higher qualification and have either worked in an internship for at least 12 months or have completed at least three years in an accredited training programme.
Doctors who have achieved a Certificate of Experience from Australia, New Zealand, South Africa, Pakistan, Sudan, Malaysia, the UK or Malta.
Doctors who aren’t eligible under the higher qualification or Certificate of Experience routes, can apply for the Pre-Registration Examination System (PRES) exam. Please see links for information on PRES and exemptions from PRES.
The following list of supporting documents will be required:
- Notarised copy of your passport.
- All Non-EU applicants must have their medical degree verified by EPIC
- All Non-EU applicants must have their internship (and if applicable their Higher Qualification diploma verified by EPIC)
- Certificate of Good Standing to be sent directly to the Medical Council, from each medical council you have worked under within the last five years. (From any authority you have been registered with.)
- International English Language Testing System (IELTS) certificate dated within the last two years with an overall band score of 7.0 and a minimum score of 6.5 in each module. OET certificate is also accepted and you must have a score of B in each module.
- Please note that all documents for Non-EU applicants outside of your EPIC verification documents must be sent to the Medical Council by post. (This includes notarised passport, English language evidence and Certificate of Good Standing), please do not email these documents.
- The address details for sending documents is : Medical Council, Upper Ground and 5th Floor, Block 9 (Europa House), Harcourt Centre, Harcourt Street, Dublin 2, D02 WR20.
Doctors Trained in the EU/EEA
If you have trained in the European Union (EU) or European Economic Area (EEA), you will be asked to create an account through our secure online facility.
You then need to complete an online application form and submit the following documents to support your application:
- Notarised copy of your passport.
- Translated and notarised copy of your original medical degree.
- Certificate of conformity stating that your training is in accordance with the EU directive 2005/36/EC (this does not apply to you if you completed your training in the UK).
- Certificate of Good Standing to be sent directly to the Medical Council, from each medical council you have worked under within the last five years.
Specialist Registration
Doctors Who Completed Specialist Training Outside of the EU/EEA
If you have either trained outside of the EU or EEA or have gained part of your training and experience in the EU or EEA, you will need to apply for specialist registration. Doctors who completed training outside of the EU or only partly in the EU must proceed via the The Category E route by requesting an application pack. This is a portfolio based application which will be assessed by the relevant training body in Ireland. Please request an application pack via our contact form.
Doctors Who Completed Specialist Training in the EU/EEA
If you have trained or are recognised as a specialist in the EU or EEA, you will have your qualifications automatically recognised by the Medical Council. You will be asked to create an account on the Irish Medical Council’s website to complete an online application form.
The following list of supporting documents will be required:
- Notarised copy of your passport.
- Translated and notarised copy of your original medical degree.
- Translated and notarised copy of your original Certificate of Specialist Training (if you are applying for Specialist Registration).
- Certificate of conformity stating that your training is in accordance with the EU directive 2005/36/EC (this does not apply to you if you completed your training in the UK).
- Certificate of good standing to be sent directly to the Medical Council, from each Medical Council you have registered and worked within during the last five years.
Next Steps
We have a dedicated compliance department to assist you with all your documentation should you be relocating to Ireland. If you can’t find the information you are looking visit www.medicalcouncil.ie.
